Scientists Discover the Difference Between Men and Women
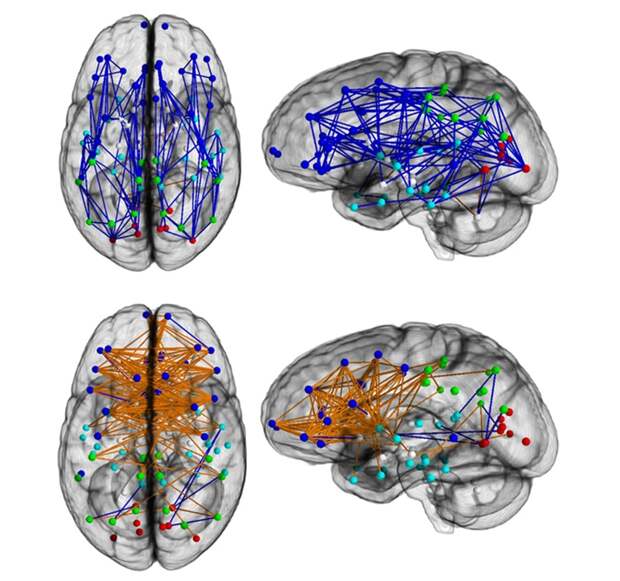
In a
study published in the
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers mapped out the structural connectome of the human brain and discovered a blatant difference between male and female neural connectivity. The study concluded that male brains are optimized for intrahemispheric communication and female brains for interhemispheric communication, or simply put: Neural connections in the male brain run between the front and back, and neural connections in the female brain run from side to side.
So what does this mean? According to colleagues at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, males are better at perception and coordinated action, and females are better at facilitating communication between analytical and intuitive processing. To put it in layman's terms: Men are better at motor skills and women are better at intuition. So the stereotypes of men being better at following directions and women making decisions based on gut feelings are actually hard-wired into our brains. In the words of co-author and 30-year veteran on gender differences, Ruben C. Gur, PhD, "It’s quite striking how complementary the brains of women and men really are.”
Men Are Better At:
- Learning a new task
- Performing a single task
- Following directions
- Spatial processing
- Sensorimotor skills
Women Are Better At:
- Memory
- Attention
- Social cognition
- Multi-tasking
- Intuition
One of the most significant finds in the study showed that the differences in neural connectivity start to increase in early adolescence, meaning boys and girls have very similar brain structures until they become teens. Very few gender differences were observed in children younger than 13, but the differences were more pronounced in participants aged 14 to 17, and became even greater in participants over the age of 17.
The study researched 949 individuals (521 females and 428 males) aged 8 to 22 years using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). DTI is a fairly new brain-scanning technique that traces the fiber pathways connecting different regions of the brain. It ultimately allows researchers to see how the entire brain is connected. You can purchase the full study from the
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Or Read the press release from Penn Medicine
here.
Понравилась статья? Подпишитесь на канал, чтобы быть в курсе самых интересных материалов
Подписаться